
03 May 2024, Friday
Comparing throughput of memory mapped file to buffered read
I have wondered about the performance of memory mapped files compared to buffered read for sequential access pattern. This is normally encountered when large files are processed sequentially, such as machine learning training. For instance, tokens for training large language models (LLMs) are read sequentially from multiple data files, and we have to iterate over these tokens several times.
While memory mapped files provide a convenient way for random
access pattern over large files, is it still the best option when
accessing files sequentially? Linus Torvalds feels that
mmap() may not always be the most performant (see [1] and [2]).
The following is an attempt to measure and see the performance, measured as gigabytes per second (GB/s) throughput for few specific access patterns. The access patterns are:
mmap()ed fresh
for each repeat, and performance measured for the sequential read
iterations in each repeat.mmap()ed once,
and we measure the performance for all sequential read iterations in all
the repeats.mmap()ed once,
but we do not access the data sequentially, jumping from one page to the
next sequentially.read() system
call to access data sequentially, however, we vary the buffer size
used.Note here that for the memory-mapping, we used the default page size,
which was 4096 bytes on my
system. I still need to run the test using larger page sizes, by
activating the options MAP_HUGETLB,
MAP_HUGE_2MB, and MAP_HUGE_1GB (see
man mmap, or Man page
for mmap()). On my system, the allowed huge page sizes
are:
$ sudo ls /sys/kernel/mm/hugepages
hugepages-1048576kB hugepages-2048kBFor the default page-size, the following is the result from one run:
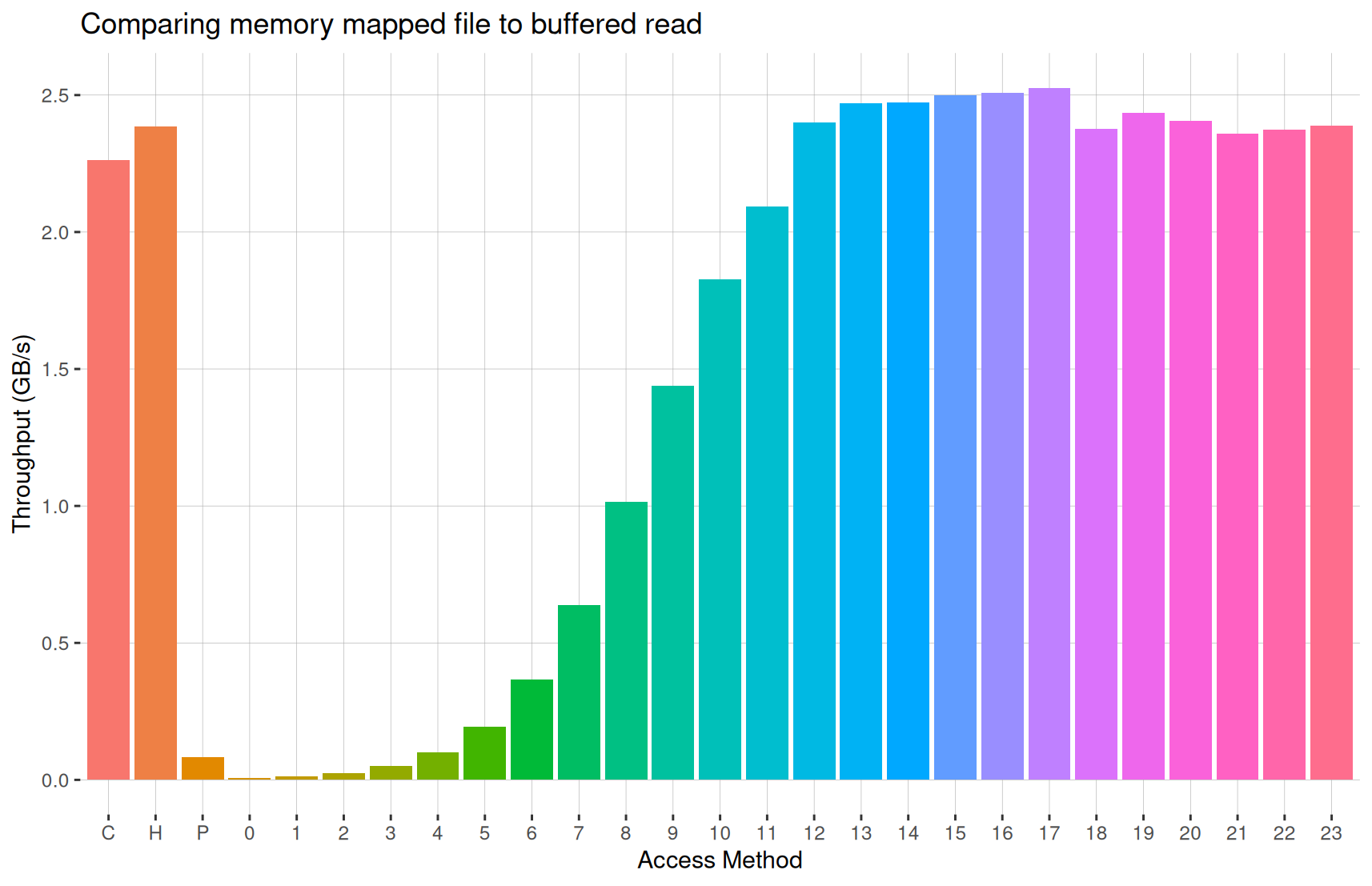
On the x-axis, the labels
C, H and P are the runs with a
memory mapped file, whereas, the numeric labels N represent
runs with a buffered read where the size of the buffer is 2N bytes.
The compilation and run are as follows:
$ gcc -O3 -o mmap_perf mmap_perf.c -std=gnu99
$ ./mmap_perf large.webm
File size: 1478286989 bytes
Page size: 4096 bytesThe complete source code is as follows:
/* Copyright 2023, Gagarine Yaikhom (MIT License) */
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
unsigned char byte; /* Stores a byte loaded from memory map */
int fd; /* File descriptor of the file used for profiling */
long page_size; /* Page size used for virtual memory paging */
double nsecs; /* Time in nanoseconds */
double total_nsecs; /* Total nanoseconds accumulated (for statistics) */
double gb_processed; /* Gigabytes processed */
char *fname; /* Name of the file provided for profiling */
char *mmap_addr; /* Address pointing to memory mapped file */
size_t length; /* File length */
size_t hist[256]; /* A histogram: to do something with bytes read */
struct timespec start; /* Records start time */
struct timespec stop; /* Records stop time */
const int num_repeats = 50; /* Number of profiling repeat runs */
const int print_granular_timing = 0; /* Should we timing for each pass? */
const double bytes_to_gb = 1.0 / (1024.0 * 1024.0 * 1024.0); /* Conversion */
#define clear_hist() \
for (int k = 0; k < 256; ++k) \
hist[k] = 0L;
#define start_timer() clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &start);
#define stop_timer(repeat) \
clock_gettime(CLOCK_PROCESS_CPUTIME_ID, &stop); \
nsecs = (stop.tv_sec - start.tv_sec) * 1e9 + \
(stop.tv_nsec - start.tv_nsec); \
total_nsecs += nsecs; \
if (print_granular_timing) \
fprintf(stderr, "%3d: %f nsecs\n", (repeat), nsecs); \
else \
fprintf(stderr, "%s", ((repeat) >= 88? "\n." : "."));
void print_throughput()
{
double average_secs_per_pass = (total_nsecs / num_repeats) * 1e-9;
double gb_per_secs = gb_processed / average_secs_per_pass;
fprintf(stdout, "\nThroughput: %.3f GB/s\n\n", gb_per_secs);
}
int open_and_size_file()
{
if ((fd = open(fname, O_RDONLY)) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open file: %s\n", fname);
return -1;
}
struct stat sb;
if (fstat(fd, &sb) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to fstat: %s\n", fname);
close(fd);
return -2;
}
length = sb.st_size;
gb_processed = length * bytes_to_gb;
return 0;
}
int mmap_hot()
{
printf("Hot mmap:\n");
total_nsecs = 0.0;
int r = open_and_size_file();
if (r)
return r;
mmap_addr = mmap(NULL, length,
PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_POPULATE, fd, 0);
if (mmap_addr == MAP_FAILED) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to mmap: %s\n", fname);
close(fd);
return -3;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num_repeats; ++i) {
clear_hist();
start_timer();
for (size_t j = 0; j < length; ++j) {
byte = mmap_addr[j];
hist[byte] = hist[byte] ? 0 : 1;
}
stop_timer(i);
}
munmap(mmap_addr, length);
close(fd);
print_throughput();
return 0;
}
int mmap_page_walk()
{
printf ("Page walk mmap:\n");
total_nsecs = 0.0;
int r = open_and_size_file();
if (r)
return r;
mmap_addr = mmap(NULL, length, PROT_READ,
MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_POPULATE, fd, 0);
if (mmap_addr == MAP_FAILED) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to nmap: %s\n", fname);
close(fd);
return -3;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num_repeats; ++i) {
clear_hist();
size_t idx = 0;
start_timer();
for (int j = 0; j < length; ++j) {
idx = (idx + page_size) % length;
byte = mmap_addr[idx];
hist[byte] = hist[byte] ? 0 : 1;
}
stop_timer(i);
}
munmap(mmap_addr, length);
close(fd);
print_throughput();
return 0;
}
int mmap_cold()
{
printf("Cold map:\n");
total_nsecs = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_repeats; ++i) {
clear_hist();
int r = open_and_size_file();
if (r)
return r;
start_timer();
mmap_addr = mmap(NULL, length, PROT_READ,
MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_POPULATE, fd, 0);
if (mmap_addr == MAP_FAILED) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to mmap: %s\n", fname);
close(fd);
return -3;
}
for (size_t j = 0; j < length; ++j) {
byte = mmap_addr[j];
hist[byte] = hist[byte] ? 0 : 1;
}
munmap(mmap_addr, length);
stop_timer(i);
close(fd);
}
print_throughput();
return 0;
}
int buffered_read(size_t buffer_size)
{
fprintf(stdout, "Buffered read (buffer size: %zu byte%s):\n",
buffer_size, buffer_size == 1 ? "": "s");
total_nsecs = 0.0;
int r = open_and_size_file();
if (r)
return r;
if (buffer_size == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < num_repeats; ++i) {
clear_hist();
lseek(fd, SEEK_SET, 0);
start_timer();
for (size_t j = 0; j < length; ++j) {
ssize_t nread = read(fd, &byte, 1);
if (nread == -1) {
close(fd);
return -3;
}
hist[byte] = hist[byte] ? 0 : 1;
}
stop_timer(i);
}
} else {
unsigned char *buffer = (unsigned char *) calloc(buffer_size, 1);
if (buffer == NULL) {
close(fd);
return -4;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num_repeats; ++i) {
clear_hist();
lseek(fd, SEEK_SET, 0);
start_timer();
for (size_t j = 0; j < length;) {
ssize_t nread = read(fd, buffer, buffer_size);
if (nread == -1) {
free(buffer);
close(fd);
return -5;
}
for (size_t k = 0; k < nread; ++k) {
byte = buffer[k];
hist[byte] = hist[byte] ? 0 : 1;
}
j += nread;
}
stop_timer(i);
}
free(buffer);
}
close(fd);
print_throughput();
return 0;
}
int print_filesize()
{
int r = open_and_size_file();
if (r)
return r;
fprintf(stdout, "File size: %zu bytes\n", length);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
int print_pagesize()
{
page_size = sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE);
if (page_size == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to determine page size\n");
return page_size;
}
fprintf(stdout, "Page size: %ld bytes\n", page_size);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "USAGE: %s <file to scan>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fname = argv[1];
print_filesize();
print_pagesize();
mmap_cold();
mmap_hot();
mmap_page_walk();
for (int i = 0; i < 24; ++i)
buffered_read(1 << i);
return 0;
}